Economy of Guptas in words of Harsh
Gupta empire was in existence from Mid-3rd century AD to Mid-6th Century BC but it was reached to its extent during the period c. 317 AD – c. 467 AD. The age of Gupta empire was characterized by elements of continuity and change in economic life. During the 1st half of the Gupta age, the economic growth continued unabatedly but around the middle of 5th century AD, the economy entered the phase of its decline. These changes were the outcome of both internal and external factors.
Also Read : Gupta Age – Foundation and Political System
Buddhism – Spread & Popularity and Its Decline
Post-Mauryan Period – Society and Philosophical Developments
Economic Life During c. 300 AD – c. 450 AD.
The Indian economy reached to its climax during this age as remarkable progress was witnessed in primary, secondary and tertiary activities of economy. The sources like Brihat Samhita of Varahmihir, works of Kalidas and Greek-Roman works etc. through light on the prosperity of economic activities during this age. The political unification provided by the Guptas helped in growth of economic activities.
The monetization of economy was highest during this age because Guptas issued largest number of gold coins but silver and copper coins also issued. Biggers ships were constructed during this age which could carry 500 peoples in one go. Roman sources informed that silk was sold in equal to weight of gold during age of Marcus Aurelius but during age of Julian it was so cheap that even commoners could afford it.
When Elrik Huna lead the seize of Rome in c. 408 AD, he lifted it after receiving 3000 pounds of pepper and 4000 rolls of silk. These references suggest that huge amount of pepper and silk was reaching Rome from India and Indo-Roman was at its climax.
Economic Life During c. 450 – c. 550 AD, the Phase of Decline
After prospering for more than 150 years, the Gupta economy was started to decline in later phase. There were various factors like politico-military, economic etc. behind the decline of the economic activities in later phase. The beginning of Huna invasion triggered the process of economic decline. Hunas were war like group, came from central Asia.
According to contemporary sources, first Huna invasion was taking place during the reign of Kumara Gupta (c. 415-455 AD). The presence of Hunas in the North-west part of the Indian subcontinent adversely affected the safety of overland routes of external trade. Demonetization of economy also contributed to the process of economic decline. Coins issued by Kumara Gupta was of poor quality as the percentage of impurity was increased in coins.
The number of coins also reduced significantly after the reign of Skanda Gupta. Decline of Roman empire in about c. 476 AD., a big shock for Gupta economy as Rome was the biggest consumer of the Indian luxuries products and trade with Romans was the source of inflow of gold in India. Because of the decline of Gupta empire, the central authority disappeared and north India got fragmented into number of principalities.
Thus, the lack of political unity significantly impacted the economic growth. The beginning of Sericulture in Rome in around c. 600 AD. reduced the demand of silk being exported by Indian merchants. Thus, the Indian silk was no more significant for Romans. The conflict of Sino-Tibetan in c. 750 AD adversely affected the Indo-China trade. Because of the reduction in the demand in trade and commerce, the manufacturing activities were severely affected.
Thus, there were numerous factors which contributed in the decline of the economy in Later Gupta age.
Gupta Coins and Their Significance
Guptas issued huge number of coins of gold, silver and copper. They issued the largest number of gold coins in whole Ancient Indian History. Gupta age coins give us various important information about the economic, social, political, religious, culture etc.
Politico-Admin Life as Revealed by Coins
Coins contains the names of kings and dates. This information helped in fixing the chronology of the Gupta age. Coins contains the titles of kings like Maharaja-Adhiraja (king of kings) and Vikram-Aditya (a title of king who defeated foreigners). These titles revealed the status and strength of Gupta rulers. The coins throw light on foreign relations of Gupta rulers.

The Licchavi princess Kumara Devi is depicted on the coins issued by Chandra Gupta, which depicted the matrimonial relations of both kingdoms. The coins issued by Samudra Gupta contain the term Licchavi Dohitra (son of the daughter of Licchavi’s), which also a proof of relation of Guptas with Licchavi.
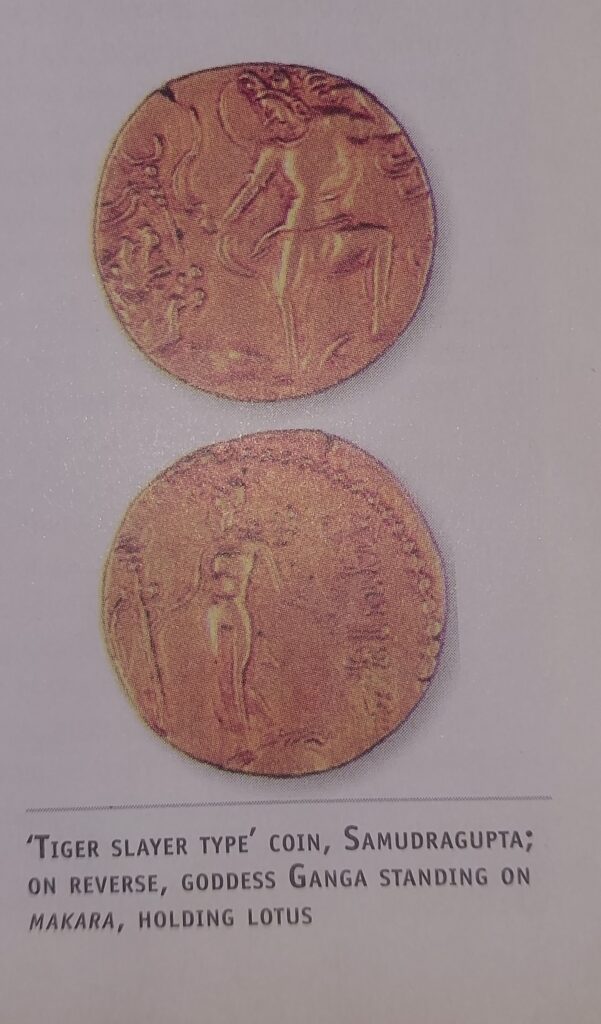
The Ashvamedha type coins issued by Samudra Gupta indicates that he was a great military conqueror and tiger slayer coins revealed that he conquered the Eastern part of India because at that time tigers were only in the forests of east India.
Socio-Religious Life as Revealed by Coins
Depiction of queens on coins revealed that the status of women was high in society. The title of Parambhagvata found on coins issued by Chandra Gupta, Garuda (vehicle of Vishnu) was emblem of Gupta’s, revealed that Guptas were followers of Vaishnavism. Depiction of Durga riding lion on Chandra Gupta’s coins indicates that Shakti worship was practiced.
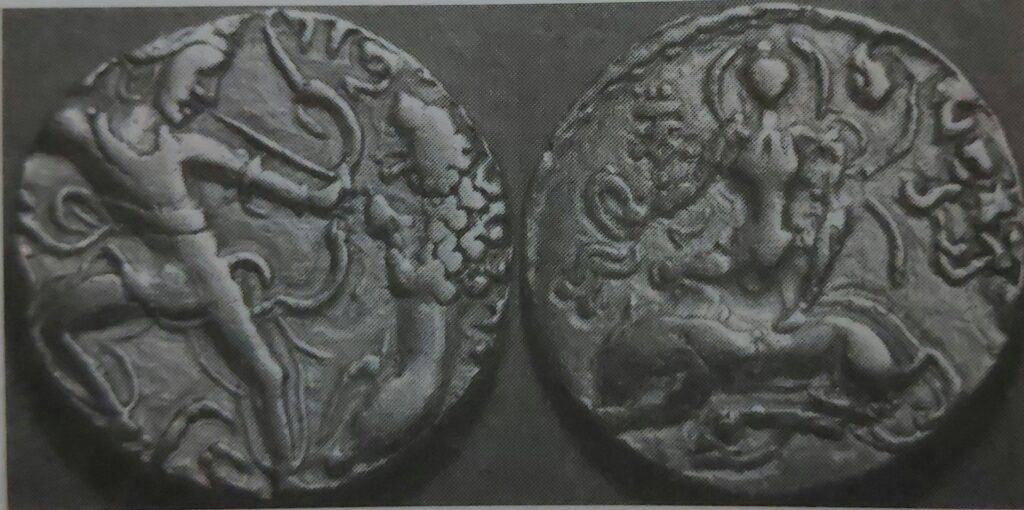

Peacock was royal emblem of Kumara Gupta as revealed by coins, which indicates that Guptas worshipped Kartikeya. Brahmanical sacrifices were performed by Guptas as indicated by the Ashvamedha type coins of Samudra Gupta.
Cultural Life as Revealed by Coins
Samudra Gupta’s coins in which he is playing Veena, indicating Guptas patronized music and Samudra Gupta was himself a noted musician of his time. Gupta’s coins are examples of miniature art as different symbols are found on coins. Script of Gupta age can also be understood with the help of coins as different names and titles are mentioned on coins.
Economic Life as Revealed by Coins
The metal used in the making of coins throw light on the knowledge of metal and metallurgy. The coins issued by early Guptas reveals the economic prosperity because large number of coins issued of gold, silver and copper. Most of the gold coins are founded from hoards which indicates that gold coins were used for the accumulation of wealth. Most of Gupta coins are discovered from towns and cities which indicates that urbanization was on its peak during the early Gupta ruler.
The land revenue was collected though the medium of kind which indicates that coins were less significant for common masses. The coins issued by Kumara Gupta was of low quality as percentage of impurity was increased in coins. This indicates that the trade and commerce started to decline, as a result overall economy was started to decline.
Thus, coins provide various useful information about the political, administration, cultural, economy etc. of the age of Guptas.

Pingback: Administration of Guptas - Nature and Character
Pingback: Gupta Age - Campaigns, Rama Gupta and War with Hunas