Sultan of Delhi and The invasions of Mongols as discussed by Harsh
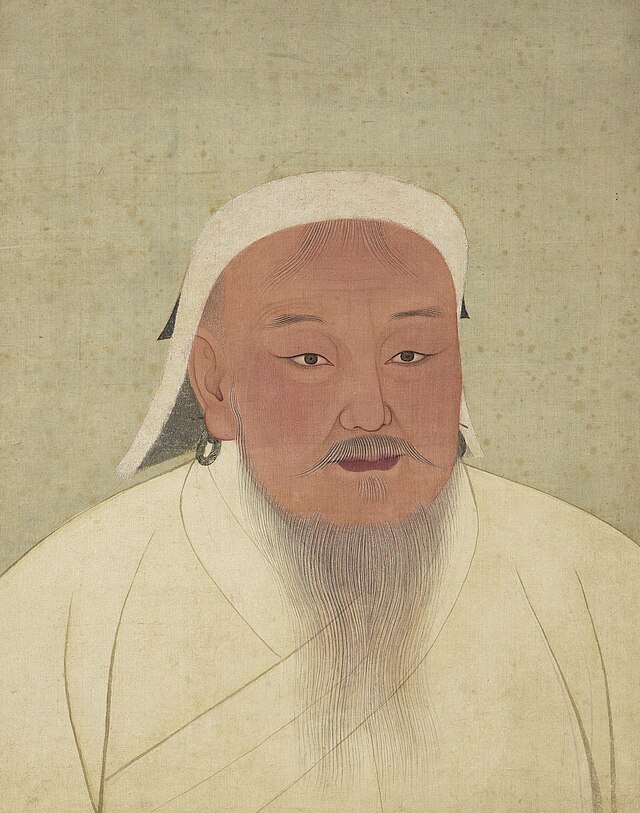

Mongols were the originally nomadic tribes of the central Asia (Mongolia). During the 13th century the rose to the power under the leadership of Chingiz Khan and built one of the largest empires in the history of mankind. By c. 1206 AD, Chingiz Khan united the Mongol and other neighboring tribes of the Turks. The Mongols also reached to Delhi for conquering India but every time they were pushed back by Delhi Sultans. Sultans of Delhi took number of steps to counter the threat of Mongols.
Also Read : The Mongol World Empire
Ghiyas-ud-din Balban – Theory of Kingship
Firoz Shah Tughlaq – An Ideal King and Decline of Tughlaq Dynasty
Invasion of Mongols to Delhi and Response of Sultans
It was Chingiz Khan who reached to frontier of India for the first time as he was chasing Jalah-ud-din Mangbarni, prince of Khwarazm, in c. 1221 AD during the rule of Sultan Iltutmish. But sultan refused to grant shelter to prince Jalah, hence by the neutrality of sultan, Chingiz Khan got impress and decided not invade India for this time. In c. 1241 AD, under the leadership of Tair, Mongols again attack Delhi during the reign of Sultan Behram Shah.
They attacked Multan first but failed to capture it, from there went to Lahore where Behram Shah sent army to counter that but they got defeat. Hence, after plundering the city of Lahore, Mongols went back. It was Sultan Balban who made elaborate arrangement for first time to counter the attack of Mongols. He first suppressed the frontier tribes who where allies of Mongols when they attack India in the north-western region.
He repaired number of forts and constructed number of new ones along frontier and placed a war ready army at these forts. Capable military commanders like Sher Khan were appointed at frontier areas. Hence, these arrangements were highly successful as when Mongols attacked India in c. 1279 and 1285, they were defeated by army of Balban. When Mongols attacked India during the reign of Kaiqubad, the arrangement made by Balban still paid off.
In c. 1292, Mongols under the leadership of Abdullah, again attacked India when Sultan Jalal-ud-din Khilji was the sultan of Delhi. To counter this attack, sultan personally went to counter the attack and defeated them. Large number of Mongols were captured. It was the reign of Sultan Alauddin Khilji, which faced serious attacks of Mongols. First in c. 1296 AD, Jafar Khan defeated Mongols. Second time, Mongols attacked under the leadership of Qadar in c. 1297 and they were defeated by Ulugh Khan appointed by Sultan.
In c. 1298, under the leadership of Saldi, Mongol attack again but they were defeated by Jafar Khan. In c. 1299, Mongol under the leadership of Qutlu Khawasa attack Delhi without engaging with the frontier forces. It was appeared that they intended to conquer India this time. Sultan Alauddin Khilji personally marched this time, during this war Jafar Khan lost his life. In c 1303, Mongols seized the Siri fort under the leadership of Targi but they went back when they failed to captured it after six months.
In c. 1306, Mongol again attacked but they were defeated by Ghazi Malik, the governor of Punjab. More than 50k Mongols were captured and sold as slaves. The last Mongol during the reign of Alauddin was in c. 1308 under Iqbal Mand but they get defeated once again and didn’t dare to attack India for almost a century. Finally, it was Timur who attacked Delhi in c. 1398 AD and captured the power as Sultan Nasir-ud-din Mahmud Tughlaq fled to save his life. The peoples of Delhi were massacred as they tried to challenge the Mongols.
This the attacks of Mongols raised serious challenges to India. The frontier of north-west India was become the concern of security. The trade and commerce through this route were severely impacted. The economy faced number of challenges as huge amount of finance went to tackle the challenges of Mongols. The link of India with the central Asian region was cut by the Mongols. Thus, Mongol’s attacks severely impacted India.

Pingback: Vijayanagara Empire - Origin, Nature and Conflicts of State