Early Medieval Age as discussed by Harsh
After the fall of Guptas as a major power in North India, the new regional principalities emerged in Indian subcontinent. The early Medieval denotes an intermediate period between the ancient and medieval period of Indian history. This period was roughly from 6th century AD to 12th century AD. During this age, new reginal empires emerged in Eastern India, North-western India and Kashmir.
Also Read : Feudal System (Samanta System) of Early Medieval India
Dark Age of Indian History (c. 200 BC – c. 300 AD) ?
Early Medieval Age – Sources and Political Narrative & Structure
Eastern India
After the death of Sashank of Bengal, much of the area went into hands of Bhaskaravarman, ruler of Assam. The areas of Bihar and Odisha went under the control of Harsha. But it was Gopala who finally founded the Pala dynasty and emerged as an important dynasty. He was succeeded by Dharmapala. Nepal was also a vassal state of Dharmapala. He also founded Buddhist monasteries at Vikaramshila, Sompura and Odtanapuri in Bihar.
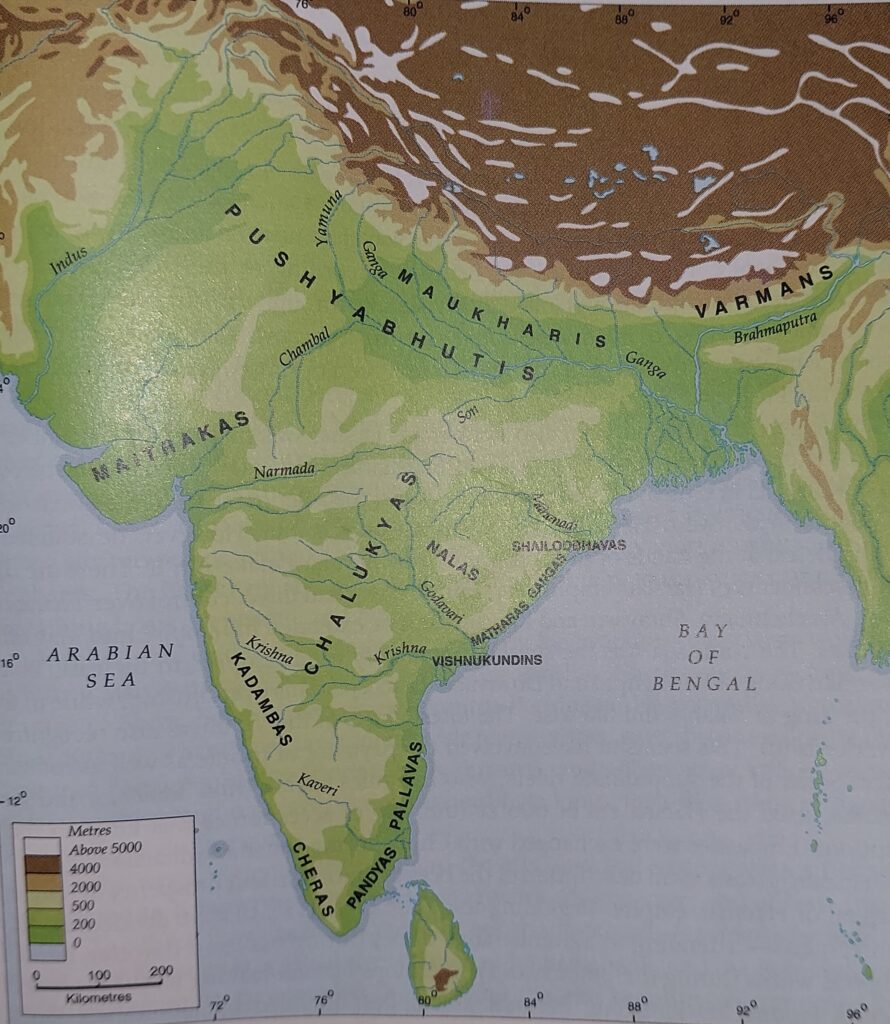
He was succeeded by Devapala who extended empire to northern India, from Himalayas to Vindhyas and from eastern to western oceans. The power of Palas decline in 9th century by suffering defeats from the hands of Rashtrakutas and Partiharas. But the power was survived by late 10th century during the rule of Mahipal but after that wipe out by 12th century AD.
Salamba Dynasty of Assam ruled from c. 800 AD to c. 1000 AD, after overthrow the rule of Pala yoke by Harjaravarman (ruler of Kamrupa) who established his capital at Haruppeshvara. In Odisha, Shailodhavas ruled during 6th century AD who were originally subordinates of Sashank. But in 10th century, Somavamshis of Dakshin-Kosala expanded their dominance.
The expansion of Ganga kingdom was begun in 10th century AD in south and north Odisha. The Ganga king Anantavarman Chodaganga were responsible for displacing Somavamshis rulers in lower Odisha in early 12th century as they were assisted by Cholas. Originally, the Ganges were the immigrants from the region of Karnataka.
Kashmir and North-Western India
The Karkota dynasty initially established their rule in Kashmir in 8th century AD which included the powerful king like Lalitaditya. The reign of king Vajraditya witnessed Arab raids into Kashmir. Jayapida claimed to defeated five chieftains of Gauda and also the ruler of Kanyakubja. The rule of Karkota was came to an end in c. 855-56 AD and they were followed by Utpala dynasty which was founded by Avantivarman.
Avantivarman was credited with having taken major step to prevent the flood waters of Mahapadma (Wular Lake). The Shankaravarman led military campaign into Punjab and Gujarat. The successor of Utpala included kings such as Yashaskara and Parvagupta.
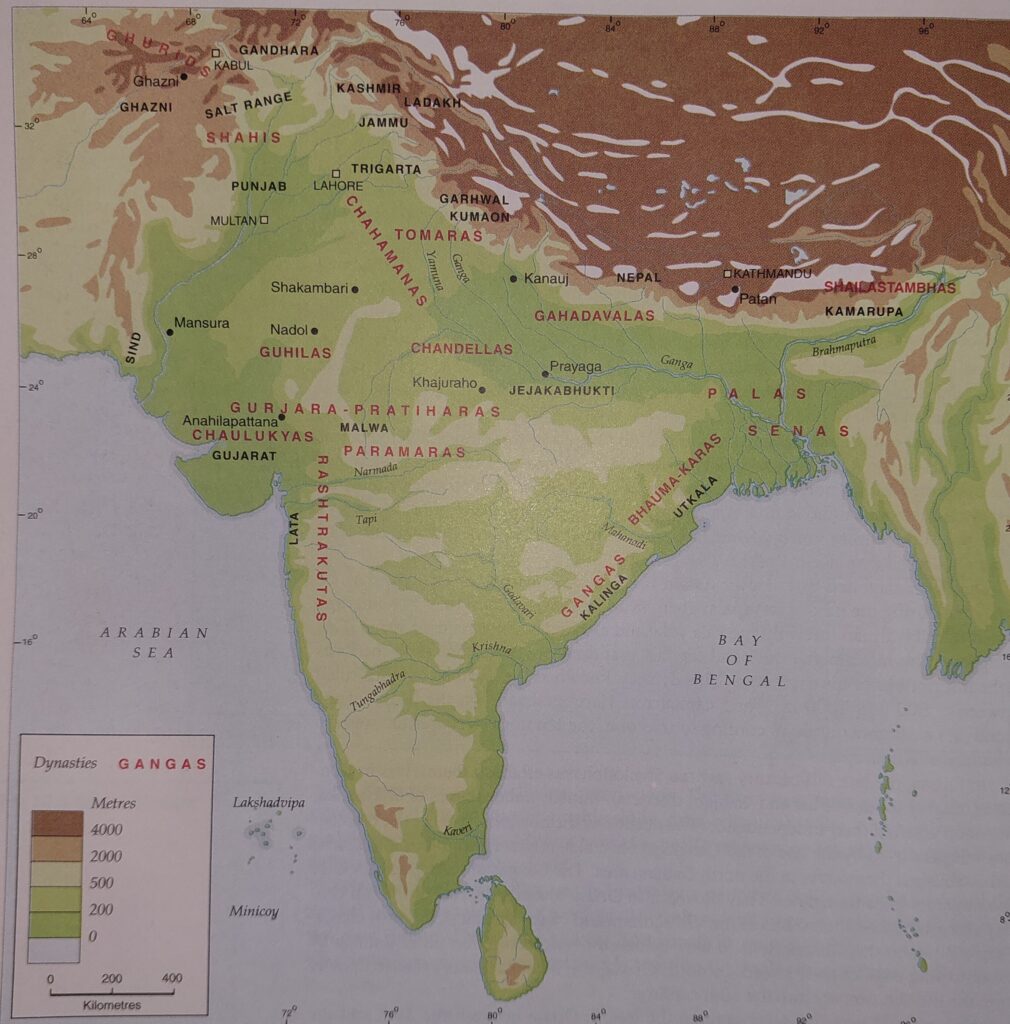
The political history of early Medieval Kashmir indicates important political role played by Tantrins (a body of foot soldiers), Ekanga (a body of soldiers who functioned as royal bodyguards) and lauded chiefs. The politics of Kashmir also included powerful king Didda who dominated the politics in second half of 10th century AD.
Shahiya dynasty, a Turkish origin, had its base in Kabul valley and Gandhara region. But in 9th century AD, Kallar overthrew Shahiya king and laid foundation of Shahi dynasty. The Kallar also mentioned in Rajatarangini of Kalhana. But this Shahi dynasty was ultimately collapsed in the wake of Ghaznavid.
Arab’s inroads into western India began with naval expedition to Thana near Mumbai. Later the conquest of Sindh was completed by Junaid who made in road towards Malwa. But thwarted by Nagabhatta, Pulakeshin and Yashovarman. In 9th and 10th century AD, much of Afghanistan was under the control of Samanids. Alptagin slave of Samanids become governor of Balkh and became independent Turkish ruler in Ghazni.
Turks succeeded in establishing a firm foothold in North-India two centuries later the reign of Muhammad of Ghor (Muhammad Ghori). Later, the Chauhans were defeated by Ghurids.
This was the starting of Turkish empire in India and the Medieval age was also commenced with it and with that new culture and art entered in Indian subcontinent which reflects in the culture of Modern-day life of Indian.

Pingback: Early Medieval Age – Rajput Clans - historylover.in