Origin of Indus Valley Civilization discussed by Harsh Kumar
The Indus Valley Civilization or we can call it Sindhu – Sarasvati Civilization or Harappan Civilization. But recently, the National Council of Education, Research and Training (NCERT) officially renamed the Harappan Civilization as the Sindhu -Sarasvati Civilization. Also, Indus Valley Civilization is used but the Harappan Civilization is completely removed from the new printed books of NCERT.
Background
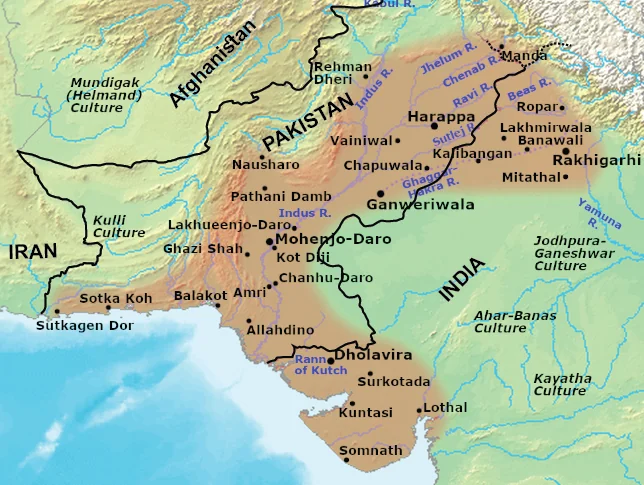
The Indus Valley Civilization was one of the oldest and greatest civilization of the world. It was discovered during the period of 1921 – 1922 by the English archeologist, John Marshall. After that Dayaram Sahni who discovered the first dedicated site of Indus Valley Civilization, Harappa, which is now under the boundaries modern-day Pakistan. It was because of that this civilization was known as the Harappan Civilization. This civilization flourished for more than 1000 years. It pushed back the Indian History to 2000 years as before the discovery of Indus Valley Civilization it was believed that the Vedic age was the first Historic age of Indian history.
Today, more than 1400 settlements of the Indus Valley Civilization have been discovered that spreading in the area of about 1.3 million square kilometers in Indian subcontinent. But the origin of this great civilization is still the topic of controversy as various historians and researchers have explained the origin of this civilization differently.
Factor behind the Controversy of the Origin of Indus Valley Civilization
The origin is the topic of controversy as the most of the evidences which are discovered are from the mature phase of the Indus Valley Civilization, as the evidences of the early phase are limited. These limited resources are interpreted by the different scholars differently. Because of this the conflict of views emerged. The most of the archeological excavation in the Indus Valley Civilization carried out in horizontal expansion of the cities of this valley. The vertical expansion less focused during excavation.
For example, the excavation carried out at Mohenjo-Daro is mainly focused through horizontal expansion. The vertical excavation is not carried out as the early site of this region is submerged underwater. Thus, under the lack of evidences of the origin of the Indus Valley settlements is not possible to not possible to trace out. Hence, different theories have emerged for explaining the origin of Indus Valley Civilization
1. Theory of Sudden Origin / Foreign Origin
According to this theory, the Indus Valley Civilization was established by the group of people coming from the Sumerian or Mesopotamian Civilization. These immigrants had the knowledge of urban life because they were living in towns and cities for a long period of time. This knowledge was used by them to built cities and town in the Indian subcontinent. This urban phase referred as Indus Valley Civilization. This theory was put forward by the scholars like R.E. Motimer Wheeler, V. Gordan Childe and Sir John Marshall.
The supporter of this theory believed that the Indus Valley Civilization attained the urban phase rapidly within a short period of time of about 500 years. This time-period was calculated by keeping in the mind the seven stratigraphic levels discovered at the Mohenjo-Daro. Such kind of development only possible when the developers have the prior knowledge of the urban developments.

Supporting Evidences of Foreign Origin Theory
The supporters of this theory put emphasized between Mesopotamian and Indus Valley Civilizations proved that works of both civilizations were of same group of people. They both were similar in their lifestyle and other features also. Both of the civilizations are urban in nature and used seals for the authentication of their transactions. They both used pictographic scripts. Potter wheel and bronze used both of them. They both used burnt bricks for the construction of houses and were contemporary of each other.
Critical Analysis of Foreign Origin Theory
The critical analysis of this provides the similarities between these civilizations are superficial in nature as there are deep rooted and fundamental differences between both the civilizations. Though both civilizations were urban in nature but Indus Valley Civilization was well-planned in nature and Mesopotamian Civilization is haphazardly built. Both the civilization used pictographic scripts but the script of Mesopotamian contains over 900 signs, which is already deciphered and Indus Valley Script contain only 396 signs, that is yet to be deciphered.
Indus Valley Civilization seals were made of steatite and were quadrilateral in shape, while the seals of Mesopotamian were cylindrical in shape and made of clay. Potters were used by both but they were different. They both used burnt bricks but the bricks of Indus Valley were bigger in size and of high quality as compared to the Mesopotamian’s bricks. The bronze used by Indus Valley was less in amount and was of inferior quality as compared to Mesopotamian civilization.
Thus, because of these fundamental differences we can say that the Indus Valley Civilization is not developed the same group of peoples of Foreign Cultures. Hence, this theory failed to provide insides on the origin of the Indus Valley Civilization.
2. Theory of Aryan Origin
According to this theory Indus Valley Civilization is built by Vedic Aryans as view put forward by the scholars like T.N. Ramachandran, A.D. Hosalkar, S.R. Rao and K.N. Shastri. They put emphasis on the evidences like both of them occupied the same area of geography. The settlement like Bhagwanpura revealed the evidence of both the Indus Valley Civilization and Vedic Aryans. They both practice agriculture. They both worshipped animal and fire. The water was scared for the ages.
Critical examination of Aryan Origin theory
This theory was never taken seriously as both the civilization have different type of living pattern and fundamentals. The Vedic Aryans were nomadic in starting whereas Indus valley peoples were living in towns, a settled life. Vedic Aryans were essentially rural but Indus Valley peoples were lived in flourishing towns. The Vedic Aryans were survived on agriculture and nomadic life whereas Indus valley peoples were indulged in the secondary and tertiary activities of economy.
The Indus Valley people used script whereas Vedic Aryans were not aware of the script. The Indus Valley peoples were phallus worshipers but Vedic Aryans hated Phallus worshippers. Harappans worshipped bull whereas Vedic Aryans worshipped cow.
3. The theory of Gradual Origin / Indigenous Origin
Recent archeological excavations carried out in North-West part of Indian Subcontinent have successfully discovered the antecedent communities and cultures of the great Indus Valley Civilization. According to this theory, the gradual evolution of the communities in last 3000 years before Indus Valley result in the development of the great civilization. This theory has been supported by the evidences of the archeologists like Walter A Fairservice, G.F. Dales, A.N. Ghosh, Stuart Pigget, Raymond and Bidget Alchin and Mohammad Rafiq Mughal.

According to this theory, the small communities were living around the North – west part of Indian subcontinent like Nal, Quetta, Mundigak, Zhob, Quli etc during the 6th millennium BC. These communities were smaller in size, economy was subsistent and represented early stage of human life. The process of evolution transformed these communities into village around 5000 BC. As the major evidences are discovered from the site of Mehrgarh.
The Mehrgarh region was semi-arid and natural resources were meager in these areas. Thus, some of the people may be migrated to the valley of Indus River. The Indus valley provide them a better environment for livelihood like better water facilities, better soil, and other natural resources like timber and minerals. This process paved way for the evolution of the society that led emergence of the cities like Kot Diji and Amri around the 4th millennium BC which represented the proto-Indus valley phase.
The process of gradual evolution resulted in the generating the agricultural surplus by around 2800 BC and by this time peoples were also started using copper tools. The surplus resulted in the development of the art and culture and help in trade and commerce activities. Thus, various centers of art and culture, and trade and commerce evolved that gave birth to the symbolic civilization of Indus Valley.
The balance involving agricultural surplus, arts, and crafts, and trade and commerce prepared the material basis for Indus Valley civilization. Till, the balance intact the civilization was continued to flourished. In starting, the Indus peoples did trade at local region but after that at around 2300 BC they starting trading with the other civilizations like Mesopotamian. This is known by the evidences from the script of Mesopotamian, as they mentioned Indus Valley Civilization as the Meluha, which identified by historians.
The balance of trade was very highly favorable to the Indus peoples as the exported in primary and secondary commodities and imported the precious materials like stones, gold, silver. This balance of trade led the prosperity of this civilization to the new heights. Harrapa, Mohenjo-Daro, Rakhigarhi, Kalibangan, Banawali, Lothal, Dholavira etc. are the major Indus Valley sites.
Conclusion
Thus, the theory of Gradual Origin of the Indus Valley civilization was widely accepted by the historians it provides the logical evidences of the Origin of the civilization as other theories failed to do so.

Pingback: Indus Valley Civilization – Nature and Character
Pingback: IVC – Indus Valley Civilization – Living Pattern -
Pingback: IVC Indus Valley Civilization – Seal and Layout of Cities
Pingback: IVC – Indus Valley Civilization – Decline and Continuity -
Pingback: Vedic Age – Origin and Political Life - historylover.in
Pingback: The Post-Vedic Age - Second Urbanization of Indian History
Pingback: Buddhism – The Teachings and Philosophy - historylover.in