Details of Megalithic culture by Harsh Kumar
After flourishing of Neolithic peoples for almost for more than 4000 years, they paved the way for the development of Megalithic and Chalcolithic age. We have already discussed the previous pre-historic ages of Paleolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic. You can read them from our website.in this article, we will be going to discuss Megalithic culture in detail.
Background
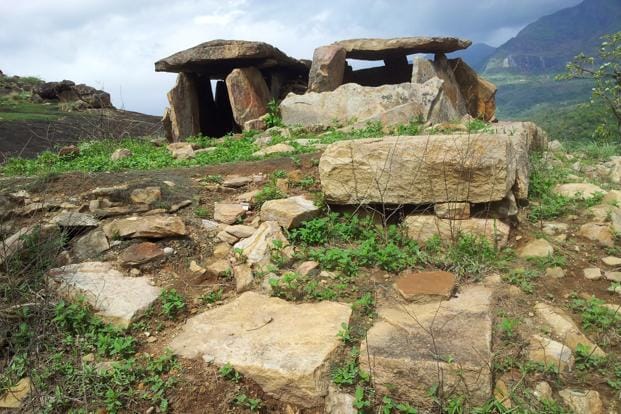

The word ‘Megalithic’ basically is the combination of two words i.e. ‘Mega’ means big and ‘lithic’ means stone. So, Megalithic means the age of big stones. This culture was flourished around 110BC to 500 BC, mainly in the Peninsular India. But evidences found in north India also. Chalcolithic culture although was flourished around 2800 BC in all over Indian continent. Chalcolithic is also made of two words i.e., ‘chalco’ which means copper and ‘lithic’ is stone, so, it means the age of copper and stone tools. The Chalcolithic culture was preceded by the Neolithic culture in Indian subcontinent around 2800 BC but Megalithic culture was preceded by Neolithic culture around 1100 BC in Peninsular region.
Megalithic Culture
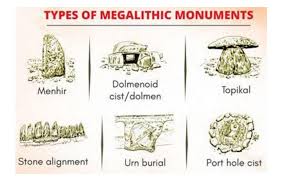
As we discussed earlier the Megalithic culture was flourished around the 1100BC to 500BC in Peninsular India. It was preceded by Neolithic age and followed by Sangam Age in Peninsular and South India. This phase was characterized by the use of big stones boulders around the graves. That’s why named as Megalithic. These boulders were used to cover the graves to further to surround it. Most of the evidences of this age are discovered from the graves, that’s why known as the Megalithic Culture.
Geographical Area Occupied and living Pattern
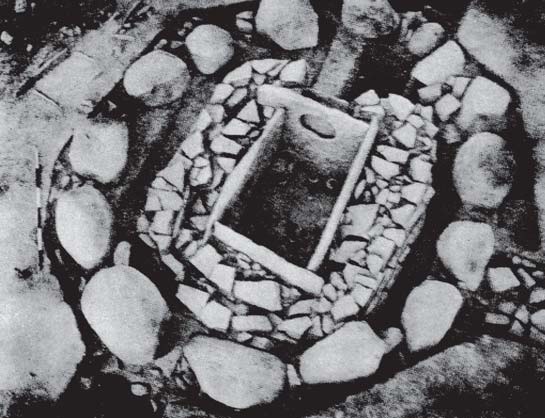

Megalithic culture covered almost all of the Peninsular India. The major sites are Jaunapani and Naikund in Maharashtra, Maski in Karnataka, Nagarjunakonda in Andhra Pradesh, Adichanallur in Tamil Nadu, Thrussur in Kerala etc., are the major Megalithic sites in Peninsular India. Apart from these Burzahom in Jammu & Kashmir also is a Megalithic site. The Megalithic peoples lived in villages. The thickness of the debris discovered indicates that they lived at a certain place for a longer period of time and after 50 to 100 years they shifted to another new places. They produced different types of food grains such as wheat and rice. They domesticated animals such as buffalo and donkey.
Material Culture and Trading during the Megalithic Age
The discovery of iron from Megalithic graves that the culture phase belongs to Iron Age. Some other metals like copper and bronze also discovered from the Megalithic sites during the excavation. Since the copper was not available in the Peninsular India that means the people of Megalithic age had trade relations with the north-west and other parts of India, particularly with Rajasthan as the copper was available in the Khetri Mines of Jhunjhunu district of Rajasthan.
They also know how to make bronze as the evidences are found or they imported it from the other parts of India like from Indus Valley Civilization. The Megalithic people used Black and Red ware pottery which was of high quality. Some of the Megalithic settlements continue to flourished till 2nd century BC. At some of the settlements, Roman coins and pottery have been discovered. These evidences suggest that the Megalithic peoples were evolved from the earlier cultures.
Thus, the Megalithic age was a short period in the history. Megalithic culture was a transition phase for the Peninsular region which paved the way for the Sangam Age in the Peninsular and South India. Megalithic people were advance in trading with other contemporary world like Roman as the evidences of such trading also discovered from the sites of Megalithic age.
